babylon
Cancellable
Principle
In the standard coroutine mechanism, co_await behaves similarly to std::future::get, where it waits for the target awaitable to complete before resuming execution. However, there are cases where we need the ability to end the wait early, such as in timeout scenarios.
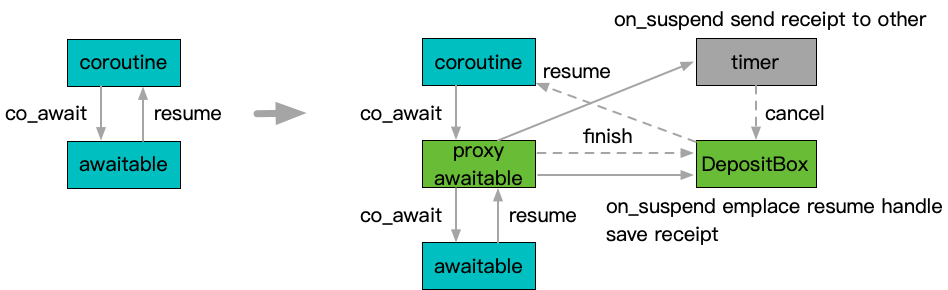
The Cancellable implementation wraps a regular awaitable and adds cancellation support by inserting a proxy awaitable. The proxy awaitable forwards co_await to the wrapped awaitable and eventually propagates the resume action back to the original coroutine that initiated the co_await. However, the proxy awaitable does not store the coroutine handle locally. Instead, it places the handle in a DepositBox and transmits it to the cancellation trigger source, such as a registered timer. When the wrapped awaitable triggers the resume, or when the cancellation source triggers the cancel, they compete for the coroutine handle stored in the DepositBox. The winning party resumes the coroutine.
Usage Example
#include "babylon/coroutine/task.h"
#include "babylon/coroutine/cancellable.h"
using ::babylon::coroutine::Task;
using ::babylon::coroutine::Cancellable;
using Cancellation = typename Cancellable<A>::Cancellation;
Task<...> some_coroutine(...) {
...
// Wrap the original awaitable as Cancellable
auto optional_value = co_await Cancellable<A>(::std::move(a)).on_suspend(
// Use a callback function to receive the corresponding cancellation handle after the coroutine is suspended
[&](Cancellation cancel) {
// Typically, the cancel handle is registered to a timer, which calls cancel() after a specified time to initiate cancellation
// From the moment the callback is executed, cancel is usable. You can even invoke cancel() directly within the callback, though it's usually unnecessary.
on_timer(cancel, 100ms);
}
);
// If 'a' completes first, a non-empty value is returned for further operations
if (optional_value) {
optional_value->item_member_function(...);
some_function_use_item(*optional_value);
} else {
// A null value indicates that the cancellation action was triggered first
}
...
}